Node Space Usage
In this section, you’ll have a better understanding of the space usage info presented by the Longhorn UI.
Whole Cluster Space Usage
In Dashboard page, Longhorn will show you the cluster space usage info:
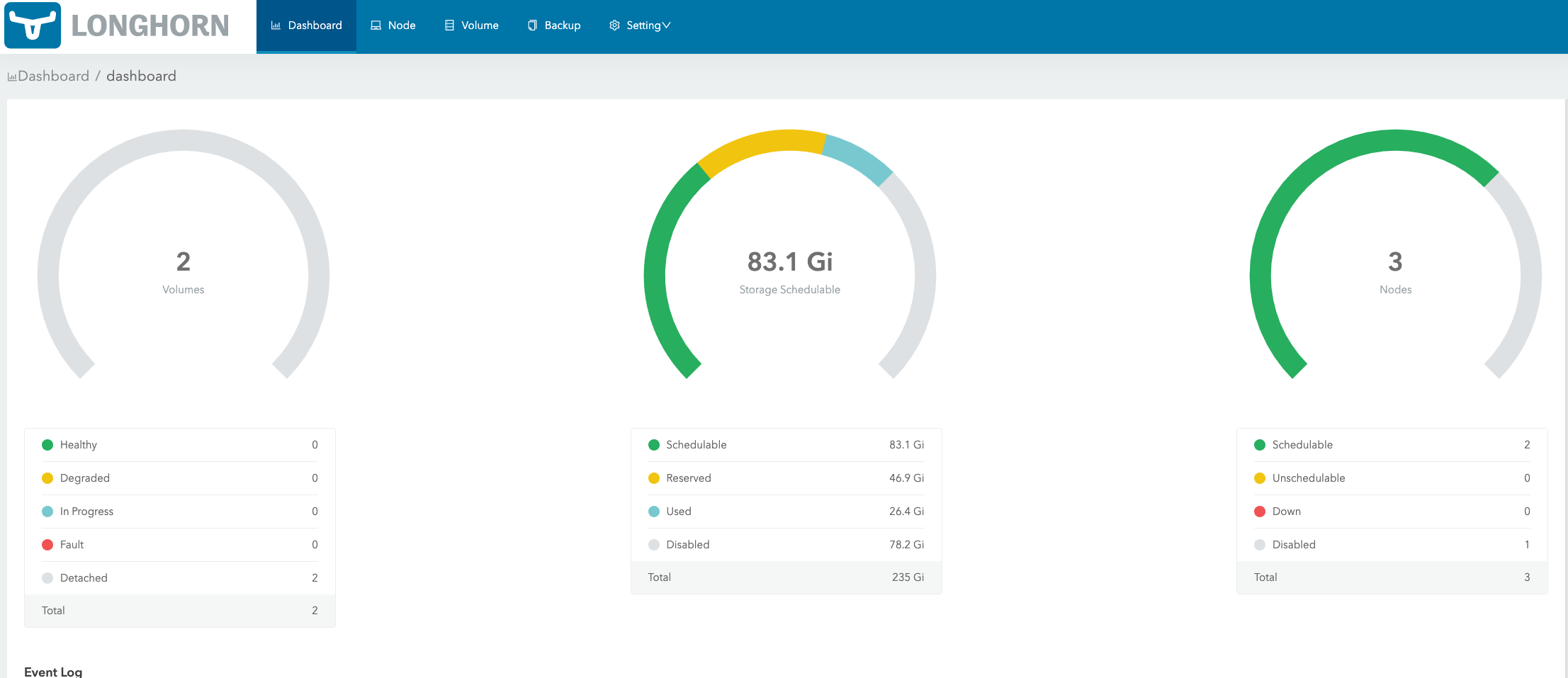
Schedulable: The actual space that can be used for Longhorn volume scheduling.
Reserved: The space reserved for other applications and system.
Used: The actual space that has been used by Longhorn, system, and other applications.
Disabled: The total space of the disks/nodes on which Longhorn volumes are not allowed for scheduling.
Space Usage of Each Node
In Node page, Longhorn will show the space allocation, schedule, and usage info for each node:
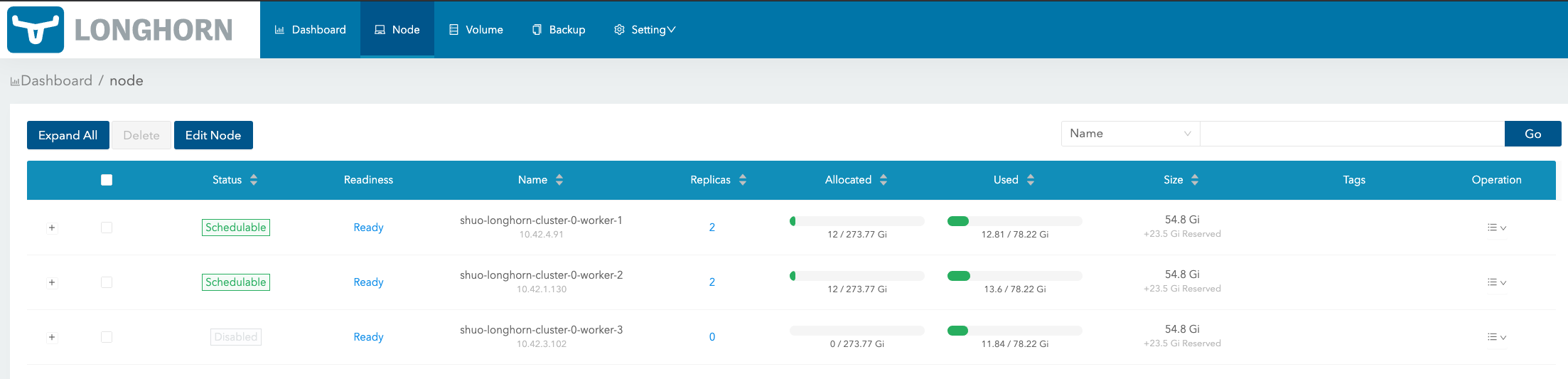
Size column: The max actual available space that can be used by Longhorn volumes. It equals the total disk space of the node minus reserved space.
Allocated column: The left number is the size that has been used for volume scheduling, and it does not mean the space has been used for the Longhorn volume data store. The right number is the max size for volume scheduling, which the result of Size multiplying Storage Over Provisioning Percentage. (In the above illustration, Storage Over Provisioning Percentage is 500.) Hence, the difference between the 2 numbers (let’s call it as the allocable space) determines if a volume replica can be scheduled to this node.
Used column: The left part indicates the currently used space of this node. The whole bar indicates the total space of the node.
Notice that the allocable space may be greater than the actual available space of the node when setting Storage Over Provisioning Percentage to a value greater than 100. If the volumes are heavily used and lots of historical data will be stored in the volume snapshots, please be careful about using a large value for this setting. For more info about the setting, see here for details.
Disk Schedulability Status and Troubleshooting Message
When a disk becomes unschedulable, Longhorn exposes the underlying reason directly in the UI.
On the Node page, if a disk’s internal Schedulable condition is False, the UI displays the exact message from node.diskStatus[x].conditions[Schedulable].
This information is essential for diagnosing issues related to space limits or over-provisioning.
Example Troubleshooting Message:
Disk default-disk-1030100000000 (/var/lib/longhorn/) on the node ip-192-168-203-144.ap-southeast-1.compute.internal is not schedulable for more replica; Scheduling space condition failed: ScheduledTotal = 4294967296 (Size + StorageScheduled) is greater than ProvisionedLimit = -64504221696 (100% of StorageMax - StorageReserved).
How to interpret this message:
ScheduledTotal: The total space currently scheduled for replicas (both existing and pending) on this disk.Note: This does not represent the actual disk usage.
ProvisionedLimit: The maximum allowed scheduling capacity for this disk. It is derived from:- the disk’s physical size (
StorageMax) - its reserved space (
StorageReserved) - multiplied by the cluster’s
Storage Over Provisioning Percentage
- the disk’s physical size (
When ScheduledTotal exceeds ProvisionedLimit, the disk becomes unschedulable and will not accept new replicas until the disk configuration or cluster settings are adjusted.
Viewing Node & Disk Space Usage via kubectl (CRs)
Longhorn exposes node-level and disk-level storage information through the Longhorn Node Custom Resource (CR). This section explains how to inspect disk capacity, schedulability, and node storage settings using kubectl.
List all Longhorn nodes
kubectl get nodes.longhorn.io -n longhorn-system
View detailed node and disk space usage
To view disk capacity, reserved space, scheduling state, and conditions for a specific node:
kubectl get nodes.longhorn.io ubuntu-lh-2 -n longhorn-system -o yaml
# replace ubuntu-lh-2 with your node name
Key fields appear under:
status:
diskStatus:
<disk-name>:
storageAvailable: # Free space on disk
storageMaximum: # Physical disk size
storageScheduled: # Total scheduled replica data
conditions:
- type: Schedulable
status:
reason:
message:
lastTransitionTime:
Note: The reserved space configured is stored under
spec.disks.<disk-name>.storageReserved.
These values map directly to those shown in the Longhorn UI.
Check disk schedulability and message
kubectl get nodes.longhorn.io ubuntu-lh-2 -n longhorn-system -o json | jq -r '
.status.diskStatus
| to_entries[]
| "Disk: \(.key) Schedulable: \(.value.conditions[] | select(.type=="Schedulable") | .status) Message: \(.value.conditions[] | select(.type=="Schedulable") | .message)"'
# replace ubuntu-lh-2 with your node name
# Sample Output:
# Disk: default-disk-4c31e9a428aa4512 Schedulable: True Message: Disk default-disk-4c31e9a428aa4512(/var/lib/longhorn/) on node ubuntu-lh-2 is schedulable
View node disk metrics in table format
kubectl get nodes.longhorn.io -n longhorn-system \
-o custom-columns=NODE:.metadata.name,DISK:.status.diskStatus.*.diskPath,AVAILABLE:.status.diskStatus.*.storageAvailable,MAX:.status.diskStatus.*.storageMaximum,RESERVED:.spec.disks.*.storageReserved,SCHEDULED:.status.diskStatus.*.storageScheduled | column -t
# Sample Output:
# NODE DISK AVAILABLE MAX RESERVED SCHEDULED
# ubuntu-lh-2 /var/lib/longhorn/ 36175872000 51409092608 15422727782 2147483648
Modify disk reserved space
To change how much space Longhorn must keep free on a disk:
- Export the node spec:
kubectl get nodes.longhorn.io ubuntu-lh-2 -n longhorn-system -o yaml > lh-node.yaml
# replace ubuntu-lh-2 with your node name
- Locate your disk entry under
spec.disksand edit:
spec:
disks:
default-disk-xxxx:
path: /var/lib/longhorn/
storageReserved: 15422727782 # update this value with something appropriate like 21474836480
- Apply the changes:
kubectl apply -f lh-node.yaml
Longhorn recalculates disk schedulability immediately.
© 2019-2025 Longhorn Authors | Documentation Distributed under CC-BY-4.0
© 2025 The Linux Foundation. All rights reserved. The Linux Foundation has registered trademarks and uses trademarks. For a list of trademarks of The Linux Foundation, please see our Trademark Usage page.